Innovation in drone (a/k/a/ unmanned aerial vehicle or “UAV”) technology has occurred at a rapid pace in the last 5 years. Cheaper and faster delivery has been one major catalyst for the heightened interest, especially among customer-centric, internet-based companies. Amazon made its first drone delivery in 2016 and other companies are getting in the game. According to research from Intelligent Automation, customers can expect 620,000 drone shipments by 2022. Package deliveries are not the only use for UAVs, by any means. Drones are in use currently in fire-fighting to reduce the risk to human firefighters, in remote surgical centers to transport supplies, and in medicine to meet an immediate need. Some healthcare providers are even experimenting with drone transport of human tissue. UAVs are of keen interest to the military as well. The U.S. Navy, for example, presently deploys drone submarines. Here, we take a look at some current and potential future applications for UAVs and the intelligent automation technology behind this ever-expanding field.
Bill Link
Recent Posts
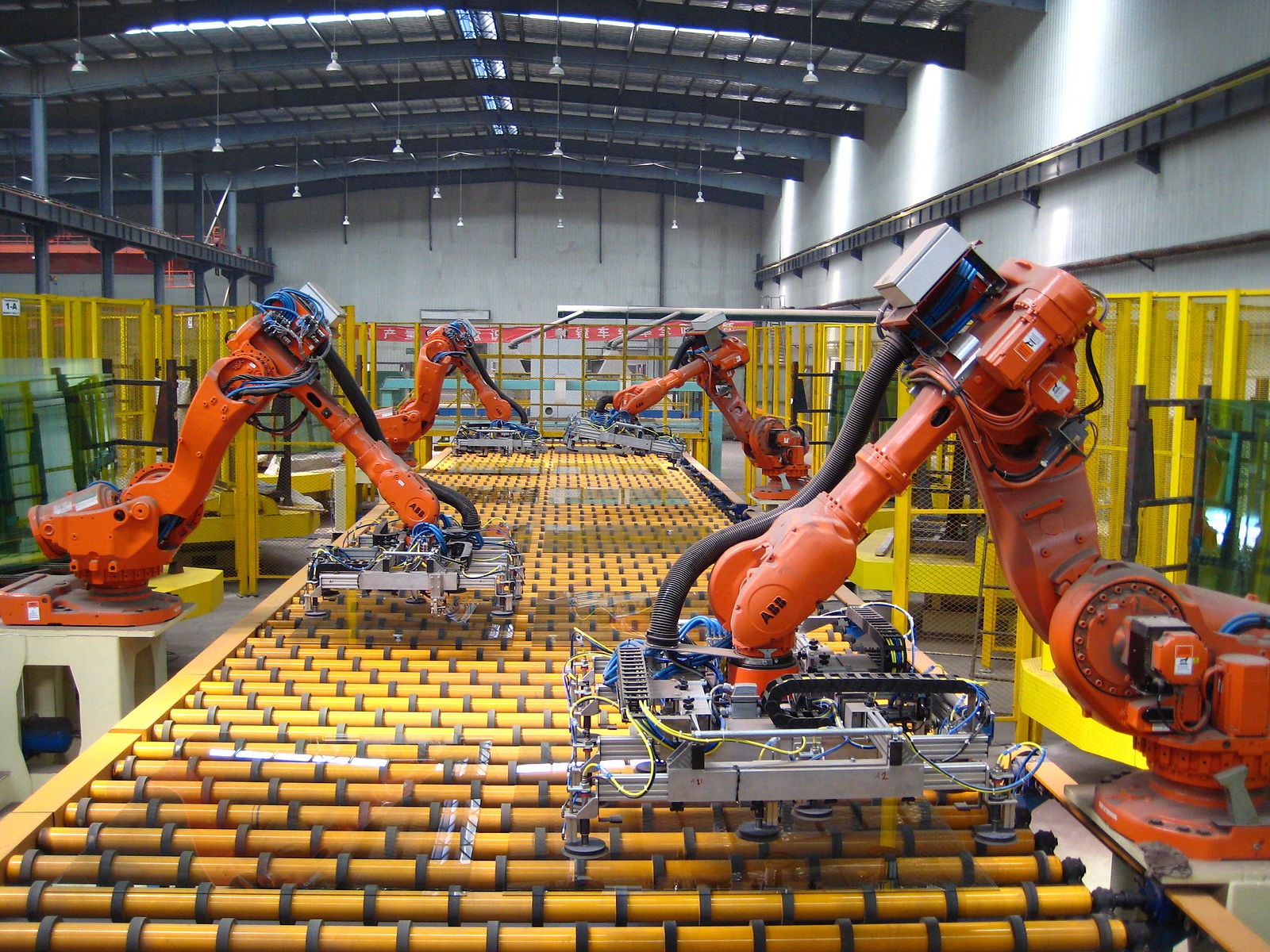
Collaborative robots (“cobots”) is the fastest growing segment in industrial automation. Cobots interact with humans in a shared workspace, whereas traditional robots function in relative isolation from human contact. Cobot operation generally incorporates various safety features like lightweight construction materials, rounded edges, limited speed and force, and sensors and software to ensure safe operation. A variety of cobot applications have emerged to improve operational efficiency, reduce on-the-job accidents and injuries, and lower operating costs. These include applications in home healthcare, warehouse maintenance, space exploration, pick and place (including material handling, packaging, and palletizing), bomb disposal, and even food preparation. Additional factors driving growth has been steadily decreasing prices and ease of implementation. Many cobots cost less than $45, 000 and, with advances in edge computing, integration costs are minimal because little or no programming may be required. In this article, we take a closer look at some of these amazing cobot applications.
As most people who keep up with the news know, the COVID19 pandemic has caused shortages in everything from cash to manufacturing supplies. Understandably, as the infection rate increased, the global focus was on finding a vaccine and securing medical supplies and equipment to save lives and slow the spread of the virus. Many manufacturers who had the capabilities switched some or all of their production to life-sustaining commodities like ventilators and face masks, which were in immediate demand. Soon it became abundantly clear that many of these critical items had been outsourced to other countries, resulting in” centers of production” abroad that have attracted many companies in the U.S. and elsewhere to reduce costs. Since the timing of economic recovery varies from country to country based on containment of the virus, vaccinations, and other factors, the ramp-up period to restart production can be significant for some manufacturers, and the resulting delays are impeding other businesses down the supply chain.
Five Tips to Using Mindfulness to Improve Sleep
Aug 26, 2021 9:33:29 AM / by posted in Self-Development
Achieving quality sleep is a challenge that many people face. Digital distraction, stress, financial problems, the pandemic and many other causes can be sources of insomnia. Having a good night’s rest can do wonders for your health, as well as your productivity, creativity, and even your ability to solve problems at work.
We have moved into a new age of space exploration thanks to the entry of business into the mix. Virgin Galactic, Blue Origin, and Space X have recognized for some time that the future focus of America’s space program must include solutions to immediate and future needs like the hazards of “space junk” from defunct satellites and other garbage left behind from astronauts, alternatives to disposal of nuclear waste and other non-biodegradable material, colonization of other planets with natural resources that are, or will become scarce, and that could sustain human life long-term in the event of a global natural or man-made disaster, and could be the launch pad for more distant place exploration. In this article, we will mention how significant achievements from private business participation in the space program are helping to address these pressing needs.
Crypto-currencies like Bitcoin have been around for a while. Yet, most people seem mystified by the concept of how virtual end-to-end transactions work. Fewer people probably have an inkling about the potential benefits/uses of blockchain technology for large organizations, particularly those with large-scale supply operations. Here, we take a closer look at the emerging uses in manufacturing, and what technological advancements we can expect in the near term.
The pandemic has proven that virtual learning (“VL”) is possible at every school. With the extremely high cost of higher education, much is being made of the need to move away from traditional models. It is unfortunate that it took a global pandemic to get countries to realize not only that VL is the way of the future, but that an overhaul of teaching and learning approaches and degree/certifications offerings is the only way American education can become relevant again, and that remaining relevancy is an ongoing effort. Advancements in technology have brought changes to nearly every aspect of our lives, including the way we learn. Innovation is as important in education as it is in any business.
The atmosphere is becoming cluttered with space debris at an alarming rate. Decades of astronauts dumping garbage into the atmosphere in orbit, as well as defunct satellites from many countries and, now, private companies, threaten future development in our atmosphere. Here we take a look at plans that might be in place, or planned, to remove human-made space debris. Further, we seek to understand the risk of an accident in the atmosphere such as a collision of defunct satellites with viable ones, and what a cleanup might look like. Space debris is an essential part of space exploration, yet few articles address the consequences of accumulating “space junk.”
The robotics market has been growing for years. That’s hardly surprising given the variety of tasks robots can handle and the demand for supplementing human effort. Robotics applications generally limited to industrial usage in its infancy, have expanded to applications such as personal assistants, surgical assistants, autonomous vehicles, delivery vehicles, crewless aerial vehicles, and exoskeletons. Valued at USD 24 billion, in 2020, the robotics market could reach USD 74 billion by 2026 quite realistically.
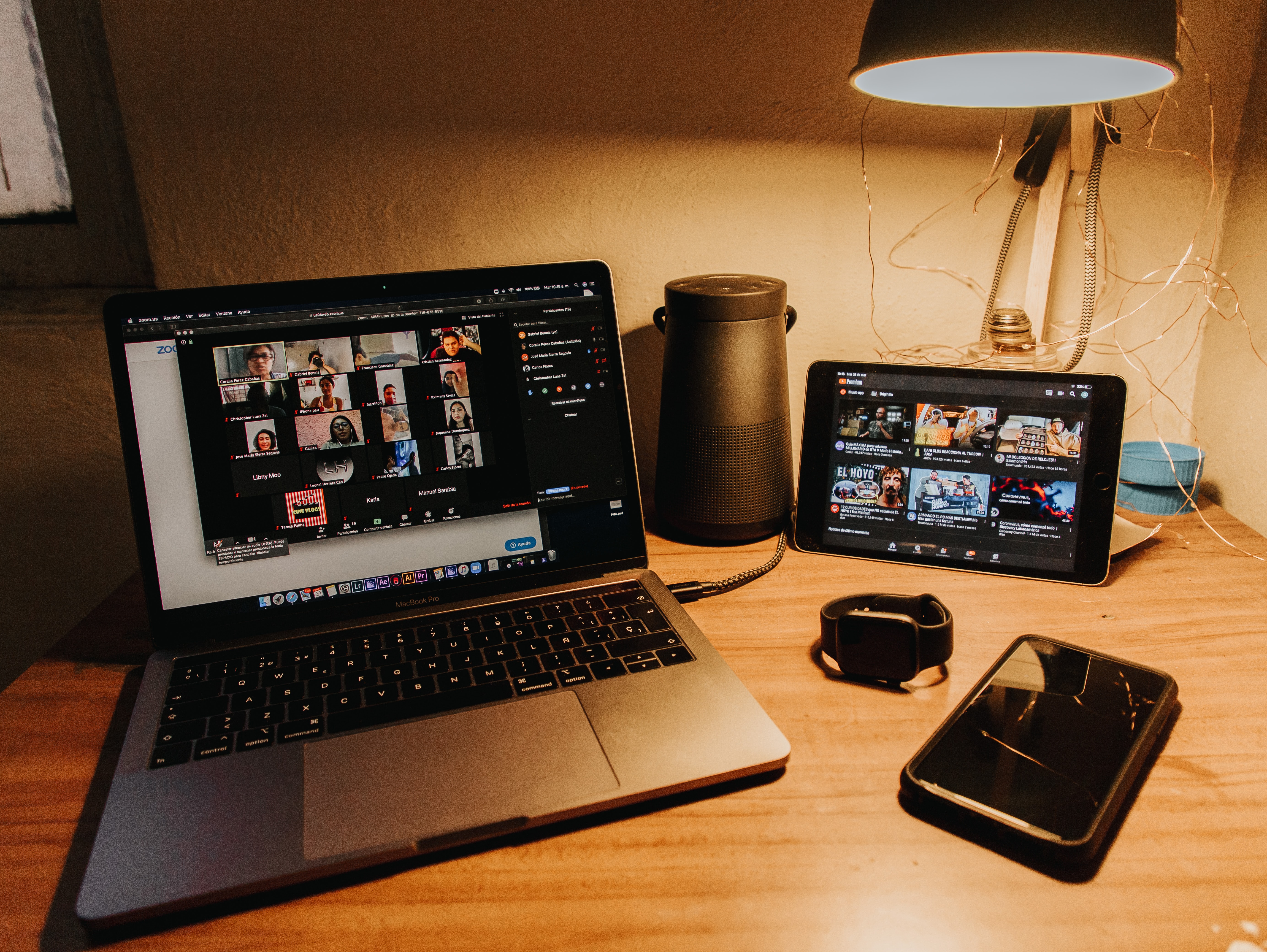
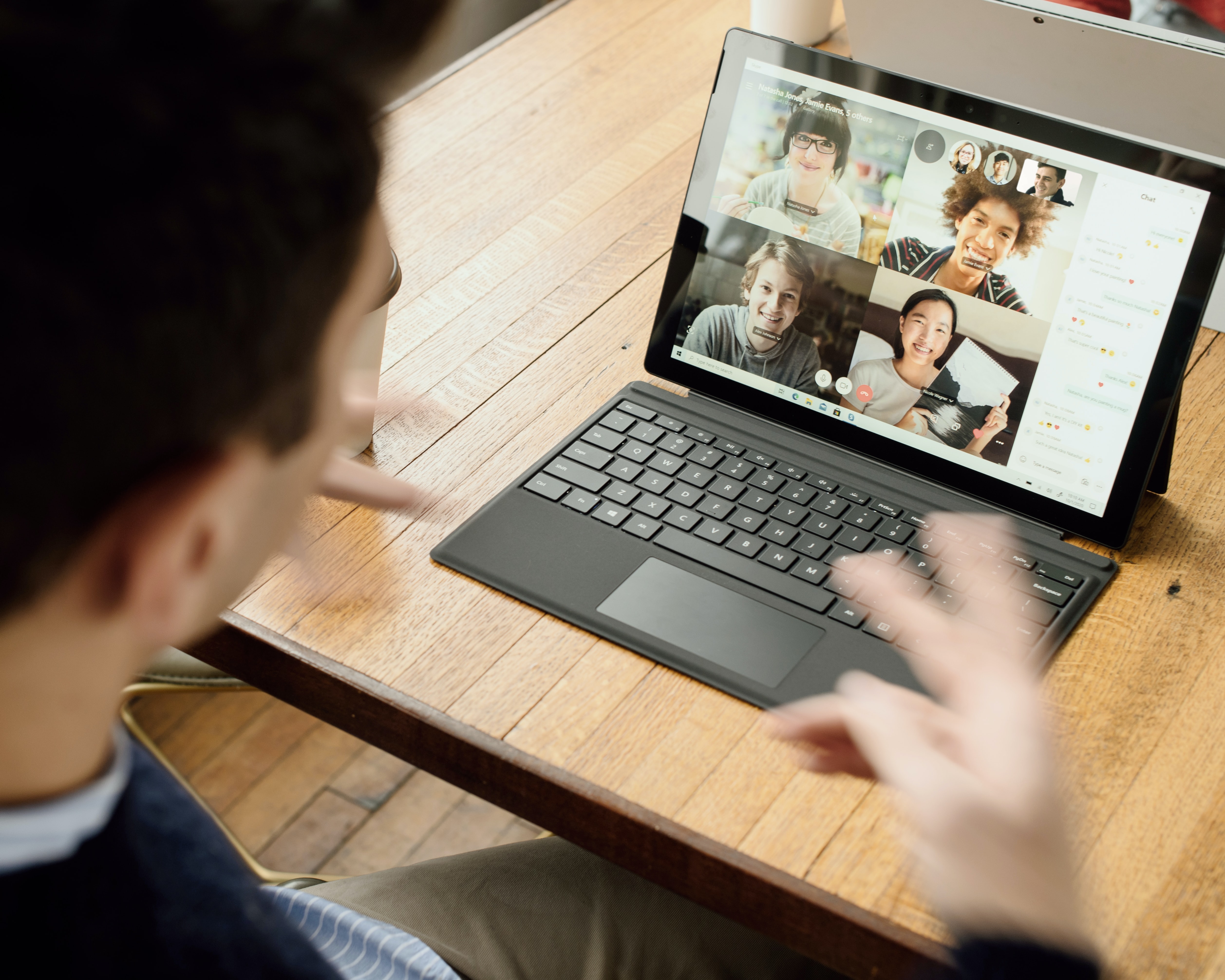
Without a doubt, the COVID-19 pandemic has been one of the most disruptive situations that many of us have faced. What was a “luxury” for executives, and a “reward” for top performers, telework has become a necessity for many organizations in the present situation. For a few years, working from home was becoming a popular option for many Americans. In fact, by 2019, about 43% of workers were teleworking at least part of the time. An additional 25 – 30% of employees have had to work from home full-time since the “lock down” began. Many companies are anticipating that telework arrangements will continue after the pandemic. Some, like REI and Nationwide Insurance, have begun to close facilities based on that expectation.